Natural Capital Evaluation

What is a natural capital evaluation?
Along the entire value chain at HUGO BOSS, important natural resources are used, along with chemical and energy inputs – from the extraction of raw materials and production to shipment of finished products. This has an impact on our climate, the quality of ecosystems and biodiversity, as well as human health, among other factors.
To live up to our responsibility, it is important to know about these impacts in detail. Fact-based knowledge is needed to set strategic priorities, make well-founded decisions, and develop sensible, more sustainable innovations.
That’s why HUGO BOSS has conducted life cycle assessments of the whole supply chains from raw materials to the final product since 2009, to examine the environmental impacts of the individual product categories. Findings by partners, scientific studies and representatives like Marzia Traverso are also included to support and validate the study. For more information, please check the three whitepapers at the end of this page. But environmental impacts – such as water consumption, land requirements, and CO2 emissions, for example – are not directly comparable, because they are measured in different units such as kilograms and litres. A further intermediate step is needed to render the different environmental impacts comparable. This is why HUGO BOSS began using the Natural Capital Protocol by the Capitals Coalition in 2016. It renders the results comparable by translating them into standardized monetary values.
In short, the natural capital evaluation identifies the steps in the value chain that cause the greatest environmental impacts. These findings form the foundation for HUGO BOSS to implement targeted measures to achieve production and distribution of its products with lower environmental impacts, for example by saving energy.
Results of the natural capital evaluation
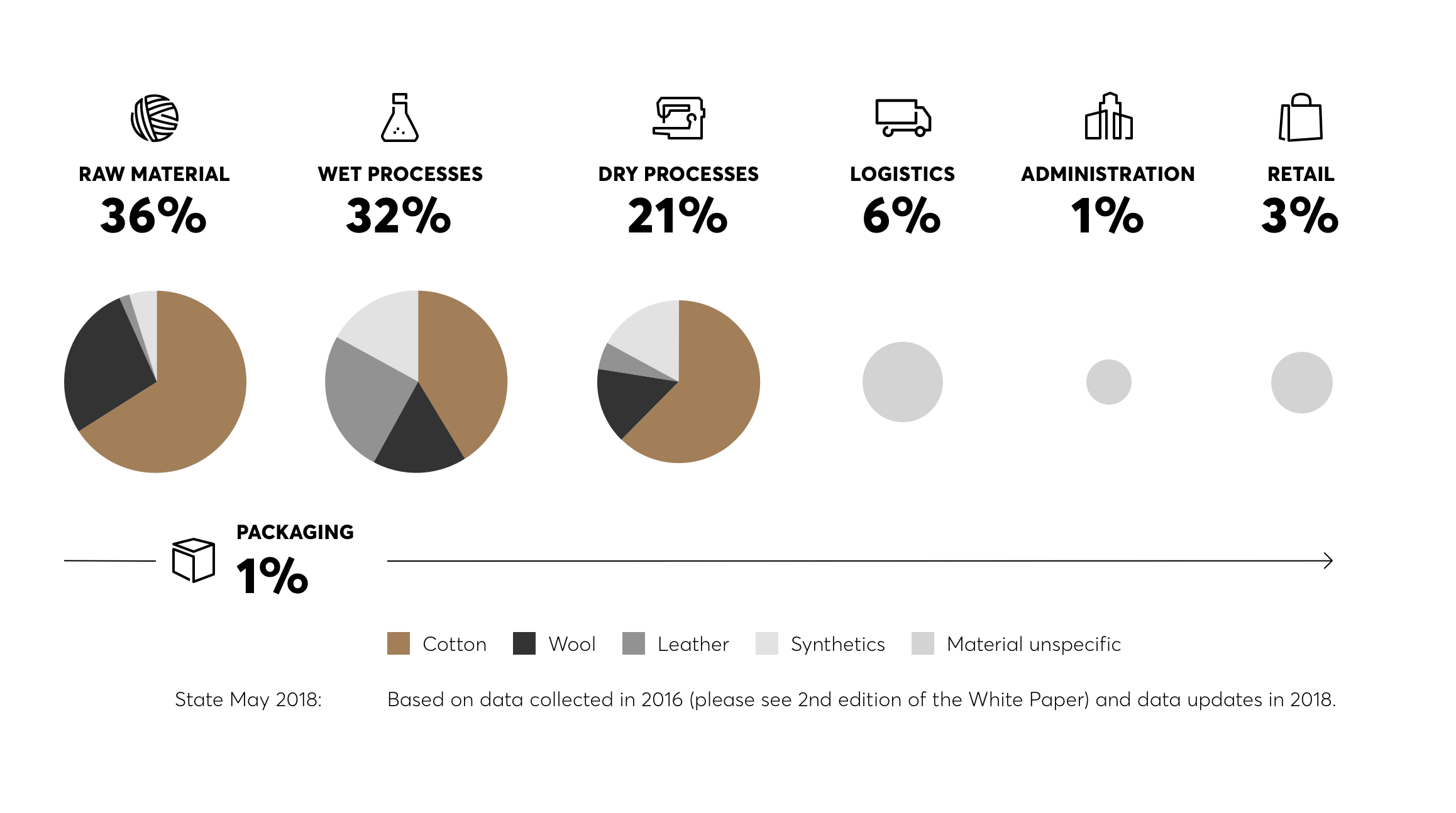
Impacts along the value chain
The greatest weight among the environmental impacts of the value chain arises during the production steps: raw materials extraction and wet and dry processes. That’s why HUGO BOSS has set special targets in these areas and become involved in relevant initiatives, such as the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) or the Leather Working Group (LWG).
For other steps in the value chain that are not directly related to products (logistics, administration, and store operation), we also aim to implement measures to reduce environmental impacts. For more information, see the PLANET section.
Impact by damage category
The different work steps along the value chain can be categorized by their corresponding ecological effects. Some of the work steps have a greater impact on climate change, for example, while others affect human health. This creates hot spots where more precise analysis and suitable measures can be employed to improve the overall environmental balance.
The largest hot spots identified in the raw materials stage are water consumption and the impact on ecosystem quality, while the wet processes have their greatest impact on climate change and human health.

-
Water consumption (raw materials)
Main drivers of environmental impacts
Growing cotton in arid areas may lead to higher water depletion without appropriate irrigation technology. Cotton plays an important role at HUGO BOSS due to its characteristics as a material: it accounts for 57% of all input materials, making it the most-used raw material at HUGO BOSS.
Measures
HUGO BOSS strives to use 100% natural materials from regenerative agriculture or closed loop recycling by 2030. When procuring cotton, we take into account the criteria of the HUGO BOSS Material Strategy. It includes regenerative cotton as a more sustainable material, being characterized by an optimized water usage among other advantages.
-
Ecosystem quality (raw materials)
Main drivers of environmental impacts
For conventional cotton cultivation, agricultural chemicals are used, such as pesticides to protect the crop against pests and fertilizers to boost its growth. However, the use of these chemicals can result in water pollution and acidification of the soil and may also pose risks to native species.
Measures
Firstly, the optimization of water consumption can already help to support the quality of the ecosystem. Secondly, as defined in the HUGO BOSS Material Strategy, regenerative cotton cultivation also entails responsible soil management and the protection of biodiversity. The production of organic cotton involves only natural fertilizers and natural means of pest control. Soil health and therewith also the preservation of biodiversity is the top priority in regenerative agriculture.
-
Climate change (wet processes)
Main drivers of environmental impacts
In the wet processes, it is primarily the energy required for procedures such as dyeing, finishing, and tanning that that can have an impact on climate change.
Measures
Leather tanning, in particular, requires large amounts of energy. That’s one of the reasons why HUGO BOSS has joined the Leather Working Group (LWG). Together we aim to increase the use of more sustainable leather. The LWG audits and certifies facilities in the leather industry that implement certain standards with regard to minimizing their environmental impact. The following aspects are taken into account during the audits: water & energy usage, waste & effluent management, air & noise emissions, traceability, health & safety, chemical management as well as restricted substances and MRSL compliance. HUGO BOSS strives to only use leather sourced from tanneries that are certified in accordance with LWG silver or comparable standards as of 2027.
HUGO BOSS also became active in the Global Climate Action for Fashion working group of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in 2018. In this group, brands, manufacturers, and organizations discuss targets and measures for climate protection along the entire textile value chain, which can contribute to the goals of the Paris Agreement.
-
Human health (wet processes)
Main drivers of environmental impacts
Tanning, dyeing, and finishing require the use of numerous chemicals, some of which have potentially negative impacts on human health.
Measures
HUGO BOSS is working on increasing the share of leather it sources from LWG-silver certified tanneries or comparable standards. In addition, the company joined the ZDHC Roadmap to Zero Programme in 2017, whose goal is to eliminate dangerous chemicals in textile, leather, and apparel production. A list of substances to avoid has been compiled by the program. This ZDHC Manufacturing Restricted Substances List (ZDHC MRSL) is now a component of all contracts with HUGO BOSS partners. You can find out more about environmental aspects in the supply chain here.
Downloads
Three white papers document research efforts by HUGO BOSS in the area of natural capital evaluation. The detailed method is described in the first version (white paper 2016). All three publications contain results for the individual product groups. In addition, the third white paper, published in 2018, describes the impacts of the HUGO BOSS value chain on climate change in greater detail.
White Paper - Environmental Impact Valuation - 3rd Edition (May 31, 2018)
White Paper - Environmental Impact Valuation - 2nd Edition (June 27, 2017)
White Paper - Environmental Impact Valuation - 1st Edition (October 07, 2016)



